Jidoka (Autonomation)
Jidoka, often referred to as “automation with a human touch,” is a key principle of the Toyota Production System (TPS) and Lean Manufacturing. In modern manufacturing practices, using the Jidoka principle reduces the defects of the product. Essentially, there are four basic elements of the Jidoka principle in lean manufacturing:
01. Detection
02. Stoppage
03. Response
04. Prevention
Let’s explore these four elements in detail:
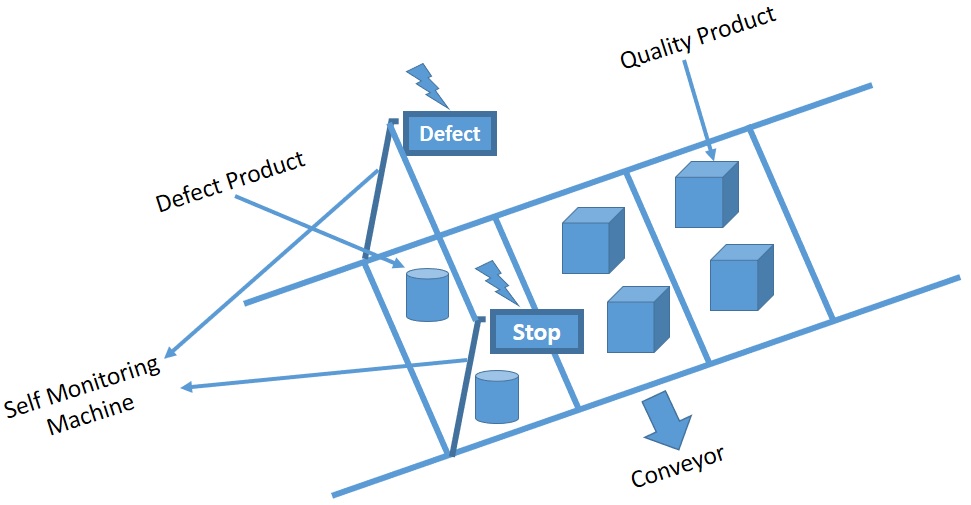
Detection of Abnormalities
Equipment should be installed with the ability to detect abnormalities. An automatic alert system should be in place to signal the operator to check and solve the abnormality as quickly as possible. Several sorts of abnormalities can be found, such as product errors, raw material defects, and potential machine failures.
Stopping Production
After detecting any kind of defect, the machine should be able to automatically stop working. The operator should manually check the defects very carefully to determine if they can be solved quickly or if they require more time.
Taking Actions
Auto-stop mechanisms impact production and help the operator determine the situation properly. The operator can call for assistance if necessary. Corrective actions should be taken within a given timeframe to resume production; otherwise, production will stop for a long time, halting overall production targets.
Jidoka Implementation in the Production Line
One of the popular Jidoka systems seen in production lines is known as the Andon system. This alert system is set up in the production line to inform the line supervisor or higher authority about quality issues. Some advanced manufacturing factories connect this alert system to mobile apps to quickly inform not only the production line in charge but also the machines department if any machine problem occurs on-site. In this way, all information on quality issues is recorded well and helps higher management take proper steps to solve these kinds of problems in the future. Previously, operators would normally fix problems themselves when a mistake caused a stop. With the practical application of Jidoka, staff members to higher management now know the quality issues very well and can place countermeasures to prevent recurrence.
Example of Jidoka
In our daily lives, most of us use modern printing machines that automatically stop when papers get jammed. Once the paper jam is cleared manually, the printer starts printing again, thereby preventing damage to its quality and the printer itself. In the manufacturing sector, one of the most famous examples of Jidoka is the Toyoda Automatic Loom Type G.
Benefits of Jidoka
01. Reduces the quality issues of the product.
02. Reduces downtime of the production line.
03. Ensures better quality of the product.
04. Prevents damage to the equipment in the production line.
