Lead Time (LT)
Lead time is one of the key factors of Lean Manufacturing. The number of days needed from placing a customer order to delivering the product to the customer is known as Lead Time (LT). Let’s go through an example with the help of a production flow chart diagram to better understand Lead Time.
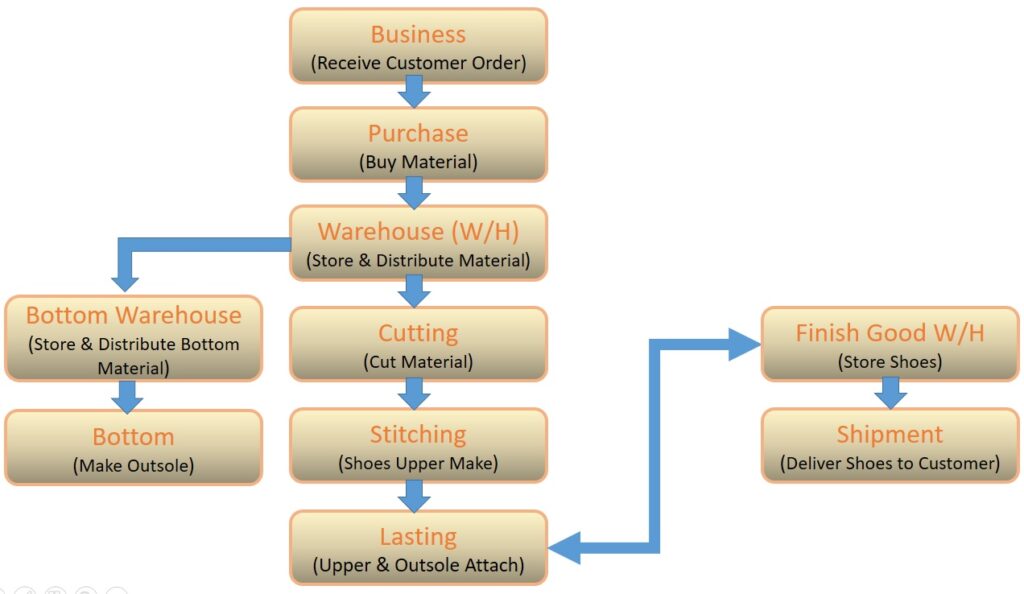
After placing a customer order, the purchase department starts to buy material. Let’s assume each section’s finish time is as follows:
Purchase – 30 days to receive all materials
Warehouse – 3 days to store materials
Bottom warehouse – 1 day to store bottom materials
Bottom – 10 days to finish outsoles
Cutting – 7 days to cut all materials
Sewing or stitching – 15 days to finish making uppers
Lasting – 7 days to make complete shoes
Finished goods warehouse – 2 days to store shoes and prepare for shipment
Customer receives the product after 20 days
Now, the lead time for this product = 30 + 3 + 1 + 10 + 7 + 15 + 7 + 2 + 20 = 95 days.
In this way, you can easily determine the lead time of a product. Remember that lead time can vary from product to product. The buyer sets the lead time based on merchandising and the total process time to complete the product. Lead time is one of the key performance indicators in shoe manufacturing because the buyer’s order amount largely depends on whether the manufacturer properly follows the lead time.
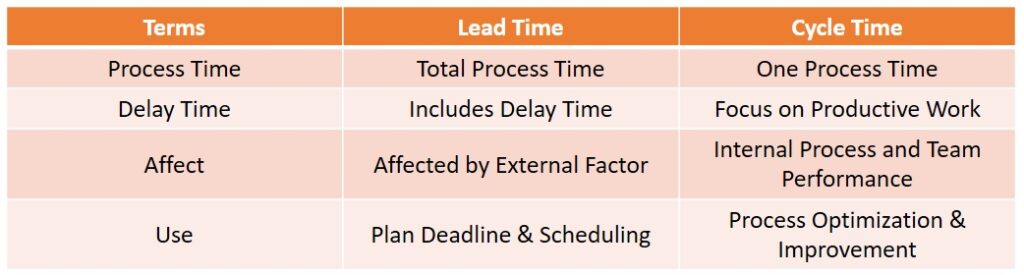
Difference Between Lead Time & Cycle Time