Andon
Andon originally comes from Japan and means “Light” or “Lamp.” In English, it is known as a “Visual Display.” In manufacturing terms, Andon refers to a signal used to alert people when a product quality issue arises. The Andon system is primarily designed to stop production when a defect occurs so that work is halted until the issue is fixed.
The aim of the Andon system is to reduce the defect rate in the production line. Furthermore, Andon enables better communication between manufacturing operators, team leaders, or external technicians in case of a machine problem in the production line. The main idea is to catch problems at an early stage and fix them as quickly as possible; otherwise, it becomes very hard to continue the production cycle.
Types of Andon
There are two types of Andon in the production line:
01. Manual
02. Automatic
Manual Andon is controlled by the operator by pressing a button on the machine in the production line.
Automatic Andon is controlled by the machine, and it automatically sounds an alarm in the production line when a product defect arises.
Cords of Andon
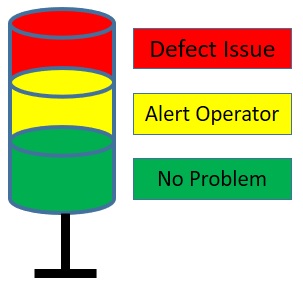
In our daily lives, we see traffic signal lights on roads, which consist of three color-coded cords. Similarly, Andon represents different lights that show the status of the problem in the production line. Most Andon boards use three color-coded cords:
Green
Yellow
Red
Green means the condition is normal, and production continues.
Yellow means a problem has been detected, alerting the operator to check the product quality.
Red means production has stopped, and the defect issue needs to be fixed as quickly as possible.
Andon and traffic signal lights are quite similar, right?
There are many real-life examples you can see around the world, such as Amazon Customer Service. They have a strong Andon system to ensure product quality. Suppose a customer reports a quality issue or a mismatch with the product description. In that case, Amazon customer service has the autonomy to “Pull the Andon Cord” and stop the shipment until the defective product problem is fixed. In manufacturing, the Toyota Andon system for car manufacturing is the most prominent example.
Impact of Andon in Lean Manufacturing
Setting up the Andon system in the production line indicates the company’s determination to produce better quality products, even if the production line stops for a short or long period. This system enables the Lean principle of built-in quality. Implementing Andon cords on the production line, connected to an Andon board usually positioned at a central place in the production line, visualizes the status of all manufacturing stations.
Benefits of Andon in Lean Manufacturing
01. Ensures better quality of the product.
02. Increases productivity and efficiency of the production line.
03. Reduces downtime and factory costs.
04. Enhances customer satisfaction.
05. Improves operators’ skills in determining product defects.
06. Promotes long-term production process improvement.
